


Next: References
Up: Network Design and Control
Previous: Covariance Structure
We have shown how transient analysis for network control (Section 5) and
design (Sections 6 & 7) can be carried out for multi-level
sources with general,
possibly long-tailed, level-holding-time distributions.
In Section 2 we analyzed the transient behavior of
a general source traffic model composed of a semi-Markov level
process and a zero-mean piecewise-stationary within-level
variation process. We approximated
the conditional aggregate demand from many
sources given system state information
by the conditional aggregate mean given level values and ages.
The within-level variation process plays no
role in this approximation.
We showed that the conditional mean can be
effectively computed using numerical
transform inversion (Section 2) and developed several approximations
to it (Sections 3 & 7). We showed how the model can be exploited
to study the value of information (Section 4).
We applied our techniques to examples in network
control (Section 5) and design (Section 7).
Even though our approach is to focus on offered load,
unaltered by loss and delay associated with finite capacity, we can
apply the conditional mean approximation in Section 2 to develop an
approximation to
describe loss and delay from a finite-capacity
system, just as described in Section 5 of [10] for the
M/G/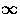 arrival process.
arrival process.



Next: References
Up: Network Design and Control
Previous: Covariance Structure
Nick Duffield
11/24/1997
![]() arrival process.
arrival process.